Polives resins special chemical backbone with hydroxyl functionality at the end of chain offers very good wetting of glassfibers carbon and aramide fibers.
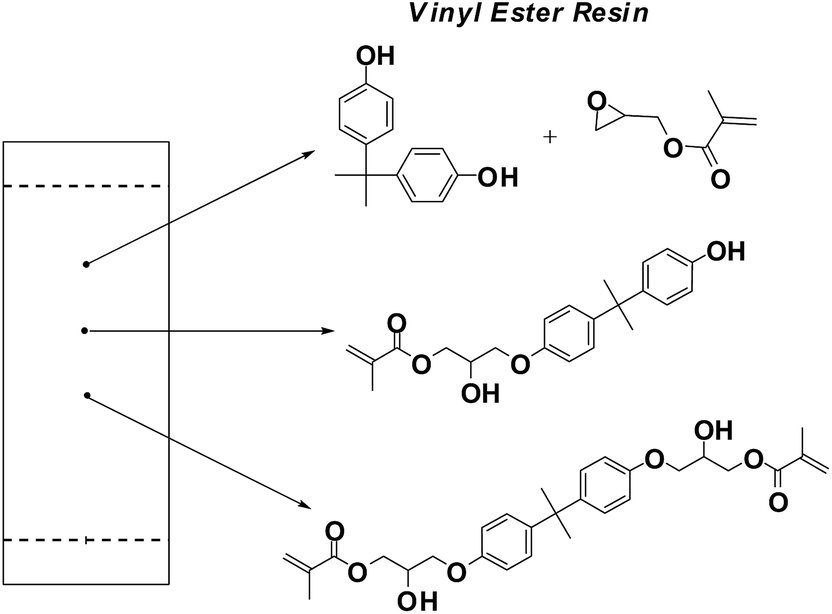
Vinyl ester resin structure.
It is also useful in hot wet fluegas environments where.
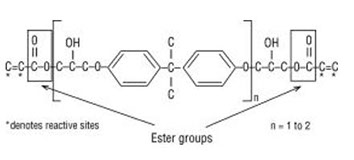
Chemical structure of the vinyl ester resin monomer.
With the reduced number of ester groups in a vinylester when compared to a polyester the resin is less prone to damage by hydrolysis.
The material is therefore sometimes used as a barrier or skin coat for a polyester laminate that is to be immersed in water such as in a boat hull.
Vinyl ester monomer contains two vinyl end groups that allow cross linked structure to form during the reaction.
To make them more workable they are typically dissolved in a vinyl monomer and occasionally a solvent 1 together with an appropriate organic peroxide.
It exhibits a corrosion resistance similar to derakane 470 resins in most environments.
As the length of the chain is available to absorb impact loads this makes vinyl ester resins more durable and resilient than polyesters.
Unsaturation at the end of the structure provides for a full cure to obtain optimum properties.
Derakane 510n resin is brominated epoxy novolac vinyl ester resin that offers a moderate degree of fire retardance1.
Vinyl ester resin or often just vinyl ester is a resin produced by the esterification of an epoxy resin with acrylic or methacrylic acids.
Essentially they comprise a base of polyester resin strengthened with epoxy molecules in the backbone of the molecular chain.
While vinyl ester resins are classified as polyester based formulations they are actually an intermediate between a polyester backbone and epoxy terminations on the ends of the molecules.
The molecular structure of vinyl ester resins is similar to that of polyesters but differs primarily on the location of their reactive groups which are positioned only at the ends of the chains.
The diester product is then dissolved in a reactive solvent such as styrene to approximately 35 45 percent content by weight.
The vinyl groups refer to these ester substituents which are prone to polymerize.
The special chemical backbone of vinly ester resins prevent hydrolysis of ester groups.
More fatigue resistant than standard epoxy vinyl ester resins.
Vinyl ester resins are relative viscous low molecular weight prepolymers.
2 the mixture is poured sprayed or molded into the final product and then converted into a thermoset by heating.
Vinyl ester is dissolved in a monomer or reactive diluent usually styrene the result is a low viscosity liquid having a solids content of 36 39.